CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) is a life-saving technique used to maintain blood circulation and oxygen delivery to vital organs during cardiac arrest. But what makes it so effective? Let’s dive into the science behind CPR and how it helps save lives.
1. The Role of the Heart and Oxygen in Survival
The human body relies on a constant supply of oxygen to function. The heart pumps oxygenated blood from the lungs to the brain and other organs. When the heart stops (cardiac arrest), blood circulation ceases, cutting off oxygen supply. Without intervention, brain cells begin to die within 4 to 6 minutes, leading to irreversible damage or death.
2. How CPR Mimics Natural Circulation
CPR consists of chest compressions and rescue breaths to manually keep blood flowing and oxygenated.
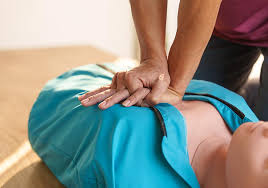
- Chest Compressions:
- Compressions push down on the chest, squeezing the heart between the sternum and spine.
- This pressure forces blood out of the heart and into vital organs.
- When the pressure is released, the heart refills with blood.
- This mimics the heart’s natural pumping action and maintains circulation.
- Rescue Breaths (for Conventional CPR):
- Provide oxygen to the lungs, which then enters the bloodstream.
- Ensures that oxygenated blood reaches the brain and other organs.
Hands-Only CPR (without rescue breaths) is also effective because compressions alone help circulate the oxygen already present in the blood.
3. The Brain’s Oxygen Dependency
The brain is extremely sensitive to oxygen deprivation. If blood circulation stops:
- After 1 minute – Brain cells start to suffer.
- After 4-6 minutes – Permanent brain damage begins.
- After 10 minutes – Survival chances are extremely low.
CPR slows down brain damage by keeping oxygen-rich blood moving, buying time until advanced medical help (such as defibrillation) arrives.
4. The Role of AEDs (Automated External Defibrillators)
CPR is critical, but it doesn’t restart the heart. It just keeps the person alive until a defibrillator can be used.
- AEDs deliver an electrical shock to reset the heart’s rhythm.
- When used within 3-5 minutes of collapse, survival rates can exceed 70%.
This is why CPR combined with rapid AED use is the most effective response to cardiac arrest.
5. Why High-Quality CPR Matters
To be effective, CPR must be performed correctly:
✅ Compression Depth: At least 2 inches (5 cm) for adults
✅ Compression Rate: 100-120 compressions per minute
✅ Allow Full Chest Recoil: So the heart refills with blood
✅ Minimize Interruptions: Continuous compressions keep blood flow stable
Poor-quality CPR can reduce survival chances, so proper training is crucial.
Conclusion: CPR Saves Lives
The science behind CPR is simple yet powerful—it keeps the heart pumping artificially, delays brain damage, and increases the chances of survival until professional help arrives. Understanding why CPR works emphasizes its importance and the need for more people to learn this life-saving skill.
Would you like additional details or graphics to go along with this topic? 🚑💓